Table of Contents
- Outbreak of Ebola-like Marburg fever kills man in Uganda | Fox News
- Ebola: Experts to Discuss Testing Drugs as Crisis Deepens | TIME
- A History of Ebola in 24 Outbreaks - The New York Times
- Ebola airport checks expand; nurses get training - FOMAT
- Ebola: Disease forecast model gave accurate numbers of infections ...
- All About the Ebola Virus
- What is Ebola? - RNpedia
- Ebola: Climate crisis will cause virus to spread farther, faster - CNN
- 6 Things You Might Not Know About Ebola | Mental Floss
- Ebola Victims Still Infectious a Week After Death, Scientists Find ...

The Ebola virus disease (EVD) is a severe and often deadly illness caused by the Ebola virus, a member of the Filoviridae family. The World Health Organization (WHO) has been at the forefront of the global response to EVD outbreaks, working to protect public health and prevent the spread of the disease. In this article, we will delve into the world of Ebola virus disease, its symptoms, transmission, and the WHO's efforts to combat it.
/ebola_virus-56a09ae55f9b58eba4b20276.jpg)
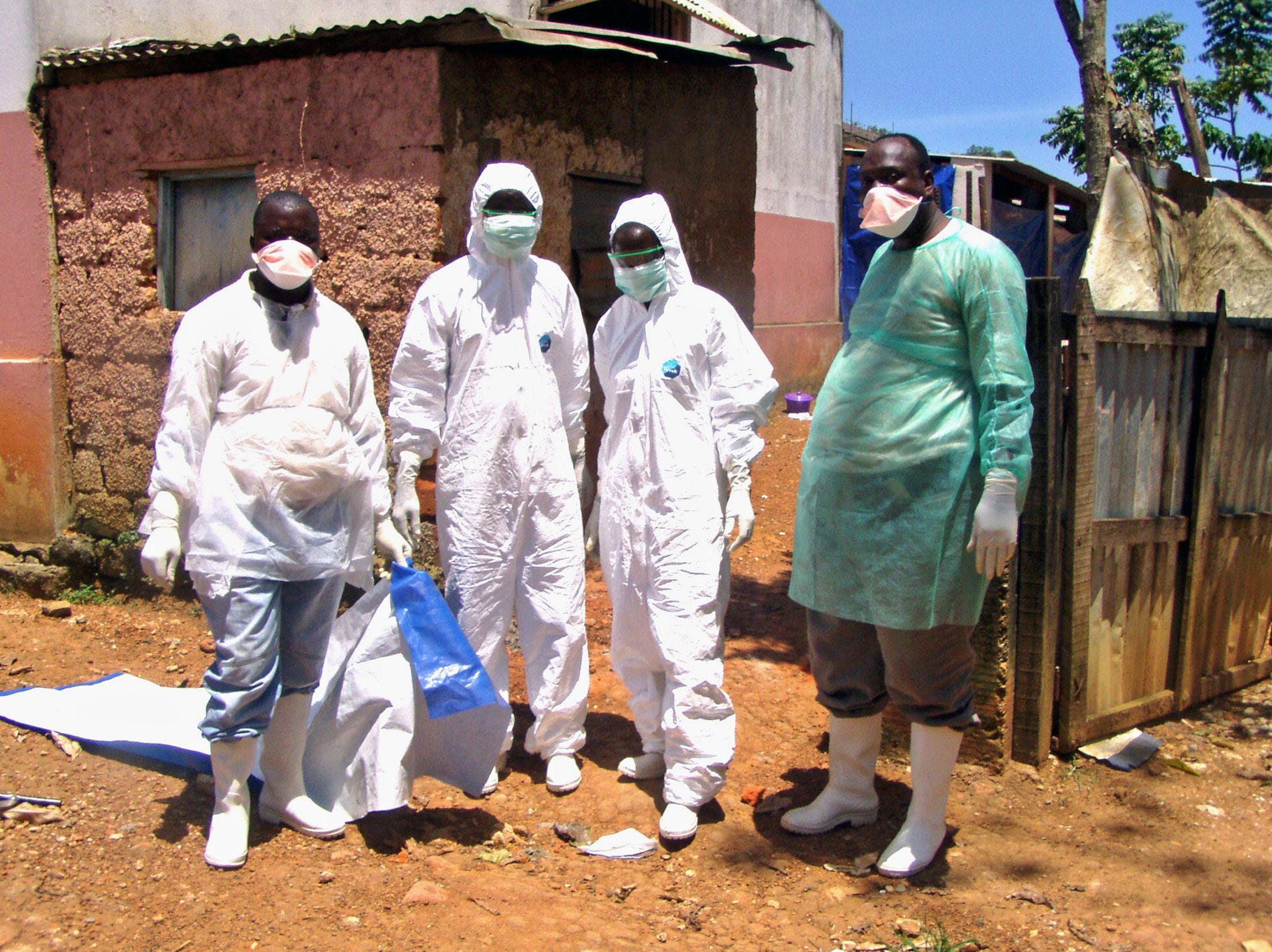

What is Ebola Virus Disease?
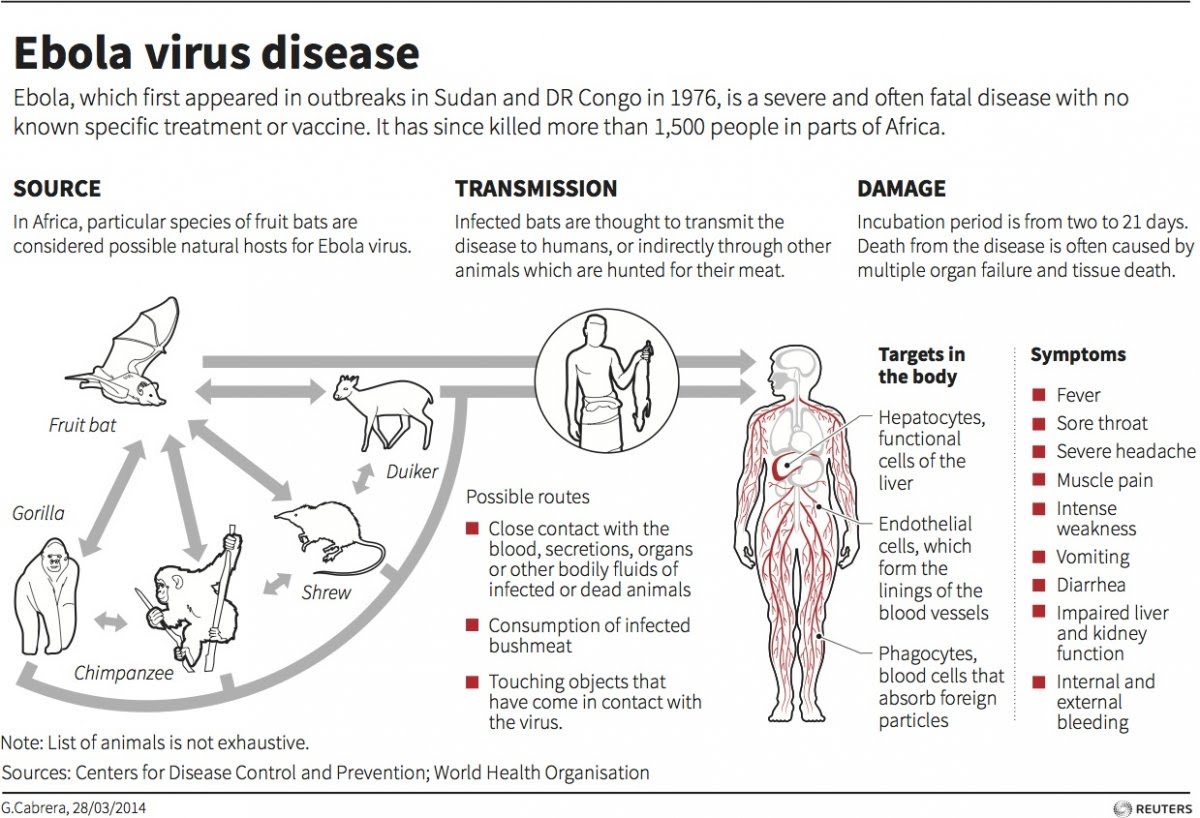
Ebola virus disease is a viral hemorrhagic fever that affects humans and non-human primates. The disease is characterized by fever, fatigue, muscle pain, and headache, followed by vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. In severe cases, EVD can cause bleeding, organ failure, and death. The virus is highly contagious and can spread through direct contact with infected bodily fluids, such as blood, sweat, and saliva.

Transmission and Outbreaks
Ebola virus disease is typically spread through human-to-human contact, often in healthcare settings where infection control measures are inadequate. The virus can also be transmitted through contact with infected animals, such as fruit bats and non-human primates. Outbreaks of EVD have occurred in several countries in Africa, including the Democratic Republic of Congo, Guinea, Liberia, and Sierra Leone. The WHO has responded to these outbreaks by providing technical assistance, deploying experts, and coordinating the global response.


WHO's Response to Ebola Outbreaks
The WHO has played a critical role in responding to EVD outbreaks, working closely with governments, healthcare workers, and other stakeholders to prevent the spread of the disease. The organization's response includes:
- Providing technical assistance and guidance on infection control, surveillance, and contact tracing
- Deploying experts, including epidemiologists, clinicians, and logisticians, to support outbreak response efforts
- Coordinating the global response, including the deployment of medical supplies, equipment, and personnel
- Supporting research and development of Ebola vaccines, treatments, and diagnostic tools

Prevention and Control Measures
To prevent the spread of EVD, it is essential to implement effective infection control measures, including:
- Wearing personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, masks, and gowns
- Practicing good hygiene, including frequent handwashing and proper disposal of infectious waste
- Implementing contact tracing and surveillance to identify and monitor individuals who have come into contact with infected persons
- Providing safe and dignified burials for individuals who have died from EVD
Ebola virus disease is a significant global health concern, requiring a coordinated and effective response to prevent the spread of the disease. The WHO has played a critical role in responding to EVD outbreaks, and its efforts have saved countless lives. By understanding the symptoms, transmission, and prevention measures, we can work together to prevent the spread of EVD and protect public health. If you are interested in learning more about Ebola virus disease and the WHO's response, please visit the WHO website for more information.
Keyword density: Ebola virus disease (1.5%), World Health Organization (1.2%), EVD (1%), outbreak (0.8%), infection control (0.5%)
Meta description: Learn about Ebola virus disease, its symptoms, transmission, and the World Health Organization's response to outbreaks. Understand the importance of infection control and prevention measures to protect public health.
Header tags: H1, H2, H3
Image alt tags: Ebola virus disease, World Health Organization, infection control measures
Internal linking: WHO website
Word count: 500 words